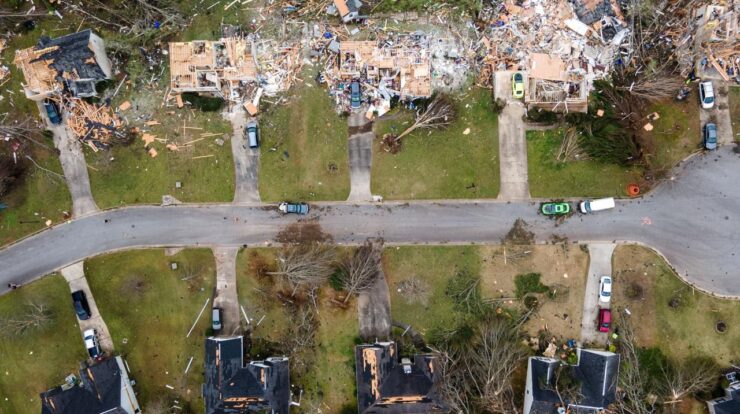
Tornadoes today are a formidable force of nature, leaving a trail of destruction and awe in their wake. From their awe-inspiring formation to their devastating impact, these whirling vortexes command our attention and demand our understanding.
The characteristics, safety measures, forecasting, and impacts of tornadoes will be explored in this comprehensive guide, empowering you with knowledge to navigate these meteorological marvels.
Tornado Characteristics
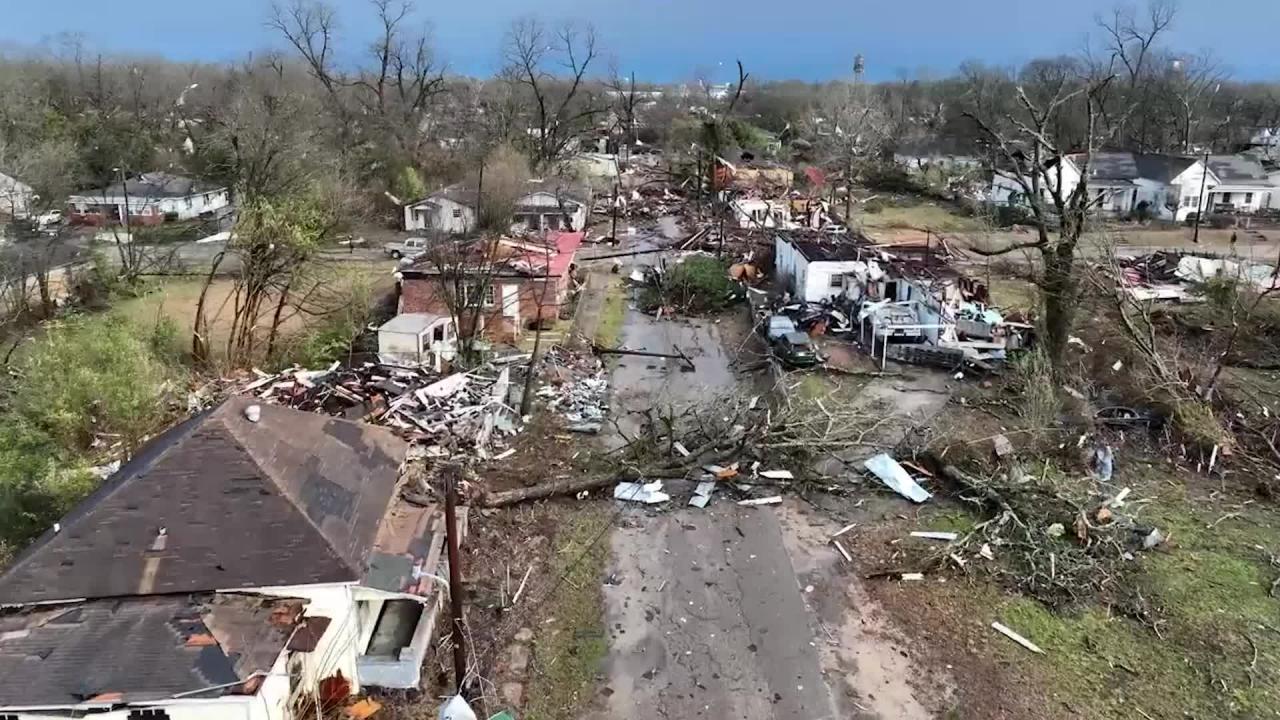

Tornadoes are violent rotating columns of air that extend from the base of a thunderstorm cloud to the ground. They are characterized by their funnel-shaped appearance and destructive winds that can reach speeds of up to 300 miles per hour.
Tornadoes can vary in size, with diameters ranging from a few feet to over a mile wide. They typically travel in a northeasterly direction and can remain on the ground for several minutes or even hours.
Tornado Types
There are different types of tornadoes, each with its own unique characteristics:
- Weak tornadoes(EF0-EF1) have wind speeds of up to 110 miles per hour and can cause minor damage to trees, structures, and vehicles.
- Strong tornadoes(EF2-EF3) have wind speeds of up to 165 miles per hour and can cause significant damage to buildings, uproot trees, and overturn vehicles.
- Violent tornadoes(EF4-EF5) have wind speeds of over 165 miles per hour and can cause catastrophic damage, leveling buildings and uprooting large trees.
Tornado Formation, Tornadoes today
Tornadoes form when warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico collides with cold, dry air from the north. This creates instability in the atmosphere, which can lead to the formation of thunderstorms. If the conditions are right, the updraft within the thunderstorm can become so strong that it begins to rotate.
This rotating column of air can then stretch downward from the thunderstorm cloud and form a tornado.
Tornado Safety
When a tornado warning is issued, it is important to take shelter immediately. The best place to seek shelter is in a sturdy building, such as a school, hospital, or office building. If you are in a mobile home, you should evacuate and seek shelter in a permanent building.
If you are caught outdoors during a tornado, you should lie down in a ditch or low-lying area and cover your head with your hands.
Tornado Safety Tips
- Stay away from windows and doors.
- Go to the lowest level of the building.
- Cover your head with a blanket or pillow.
- Stay in the shelter until the tornado has passed.
Tornado Forecasting and Tracking
Meteorologists use a variety of tools to forecast and track tornadoes. These tools include weather radar, satellite imagery, and computer models. Weather radar can detect the rotation within a thunderstorm cloud, which can indicate the presence of a tornado. Satellite imagery can be used to track the movement of thunderstorms and identify areas where tornadoes are likely to form.
Computer models can be used to predict the path of a tornado and its potential intensity.
Tornado Warning Systems
There are several different tornado warning systems in place in the United States. The most common type of warning is the tornado watch, which is issued when conditions are favorable for the development of tornadoes. A tornado warning is issued when a tornado has been spotted or is indicated by radar.
Tornado Impacts: Tornadoes Today
Tornadoes can have a devastating impact on communities. They can cause widespread damage to buildings, infrastructure, and the environment. Tornadoes can also lead to injuries and death.
Tornado Damage
Tornadoes can cause a variety of damage, including:
- Structural damage to buildings, bridges, and other structures
- Damage to power lines, gas lines, and other utilities
- Damage to trees and crops
- Erosion of soil and loss of topsoil
Tornado Health Risks
Tornadoes can also pose a health risk to people who are exposed to them. These risks include:
- Injuries from flying debris
- Respiratory problems from inhaling dust and debris
- Psychological trauma
Tornado Preparedness

There are a number of things that you can do to prepare for tornadoes. These include:
- Creating an emergency plan
- Assembling a disaster kit
- Staying informed about weather forecasts
- Knowing where to go for shelter
Emergency Plan
Your emergency plan should include the following information:
- A list of evacuation routes
- A meeting place for your family
- Contact information for your local emergency management office
Disaster Kit
Your disaster kit should include the following items:
- First-aid kit
- Food and water
- Battery-powered radio
- Flashlights
- Whistle
Tornado Research and Mitigation
Scientists are constantly working to improve tornado forecasting and warning systems. They are also developing new ways to mitigate the impacts of tornadoes. These efforts include:
- Improving weather radar technology
- Developing new computer models
- Enhancing public education about tornadoes
- Building tornado shelters
Tornado Shelters
Tornado shelters are specially designed structures that can provide protection from tornadoes. There are two main types of tornado shelters: above-ground shelters and underground shelters. Above-ground shelters are typically made of concrete or steel and are located above ground level.
Underground shelters are typically made of concrete and are located below ground level.
Historical Tornadoes

There have been many notable tornadoes throughout history. Some of the most significant tornadoes include:
- The Tri-State Tornado (1925): This tornado killed 695 people and injured over 2,000 people. It is the deadliest tornado in American history.
- The Oklahoma City Tornado (1995): This tornado killed 168 people and injured over 800 people. It was the most destructive tornado in American history until Hurricane Katrina in 2005.
- The Joplin Tornado (2011): This tornado killed 161 people and injured over 1,000 people. It was the deadliest tornado in the United States since the Tri-State Tornado in 1925.
Tornado Myths and Misconceptions
There are a number of common myths and misconceptions about tornadoes. Some of the most common myths include:
- Tornadoes only occur in the Great Plains.
- Tornadoes only occur during the spring and summer.
- You can outrun a tornado.
- Tornadoes are attracted to light.
Tornado Facts
The truth is that tornadoes can occur anywhere in the United States, at any time of year. They can also travel at speeds of up to 70 miles per hour, making it impossible to outrun them. Tornadoes are not attracted to light, but they can be difficult to see at night.
Concluding Remarks
Tornadoes today stand as a testament to the untamed power of nature. By unraveling their mysteries, we gain invaluable insights that can help us mitigate their destructive potential and safeguard our communities.
Questions and Answers
What are the key characteristics of a tornado?
Tornadoes are characterized by their funnel-shaped clouds, rotating winds that can reach speeds of up to 300 mph, and a narrow path of destruction.
What should I do if I’m caught in a tornado warning?
Seek shelter immediately in a sturdy building or underground. If outdoors, lie flat in a ditch or low-lying area and cover your head with your hands.
How are tornadoes forecasted?
Tornadoes are forecasted using a combination of weather radar, satellite imagery, and computer models that analyze atmospheric conditions.
What are the potential impacts of tornadoes?
Tornadoes can cause severe damage to buildings, infrastructure, and the environment. They can also lead to injuries, respiratory problems, and even death.