Kenya nairobi flooding – Kenya’s capital city, Nairobi, is facing a severe flooding crisis, leaving thousands displaced and infrastructure damaged. This article delves into the causes, government response, humanitarian efforts, and long-term solutions to address this pressing issue.
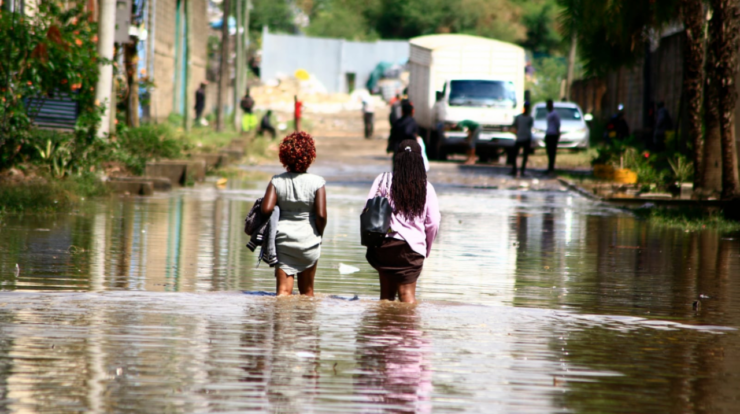
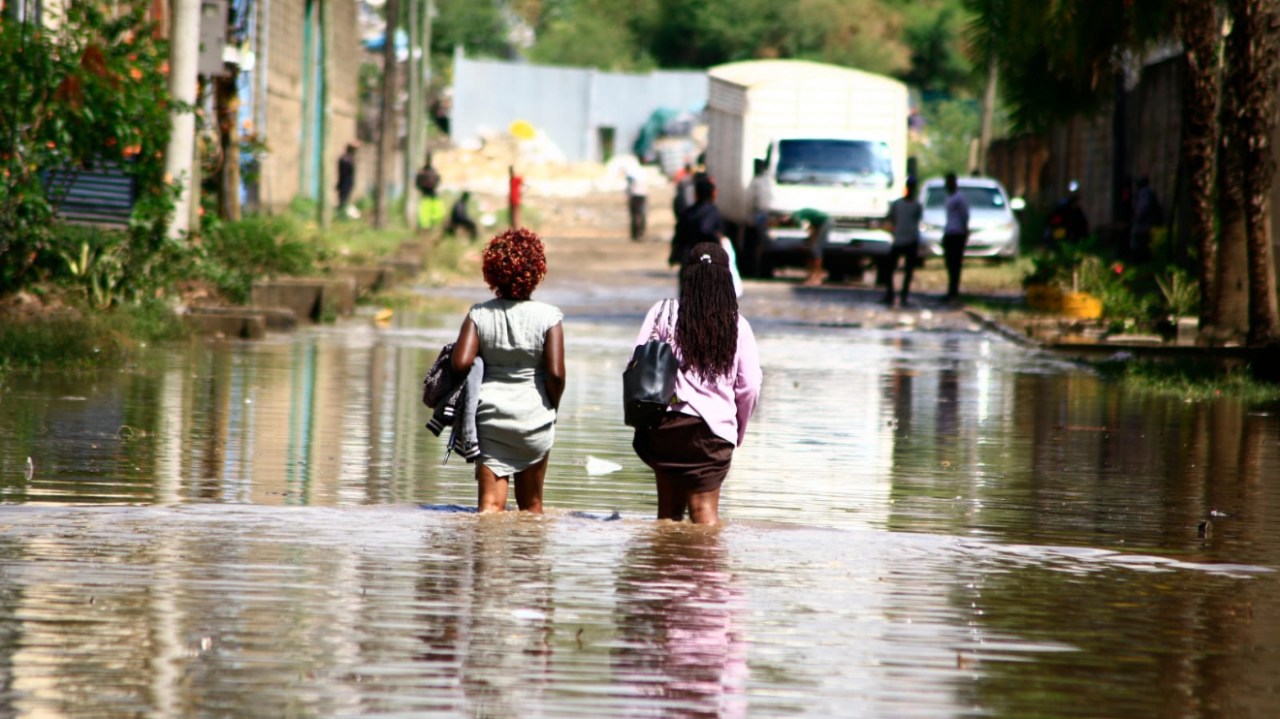
The relentless downpours have inundated vast areas of Nairobi, submerging homes, roads, and businesses. The flooding has displaced an estimated 50,000 people, destroyed over 1,000 homes, and caused significant economic losses.
Nairobi Flooding Situation
Flooding in Nairobi, Kenya, has become a recurrent crisis, causing widespread damage and displacement. The city has experienced heavy rainfall in recent months, leading to overflowing rivers and drainage systems. The flooding has affected thousands of residents, destroying homes, businesses, and infrastructure.
The worst-hit areas include Kibera, Mathare, and Kawangware slums, where poor drainage and inadequate housing conditions have exacerbated the impact of the floods. The flooding has also disrupted transportation, with roads impassable and public transport services suspended.
Causes of Flooding
The flooding in Nairobi is primarily caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Heavy rainfall:Nairobi has experienced unusually heavy rainfall in recent months, exceeding the capacity of the city’s drainage systems.
- Poor drainage systems:The city’s drainage systems are outdated and inadequate, unable to handle the increased volume of rainfall. Clogged drains and blocked waterways contribute to the flooding.
- Inadequate urban planning:Poor urban planning has resulted in the construction of settlements in flood-prone areas, increasing the vulnerability of residents to flooding.
- Environmental degradation:Deforestation and urbanization have reduced the city’s natural capacity to absorb rainwater, contributing to increased runoff and flooding.
Government Response, Kenya nairobi flooding
The Kenyan government has responded to the flooding crisis with a range of measures, including:
- Evacuation and relief efforts:The government has evacuated residents from flooded areas and provided food, water, and shelter to those displaced.
- Infrastructure repairs:The government has begun repairing damaged infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and drainage systems.
- Long-term solutions:The government is working on long-term solutions to address the underlying causes of flooding, such as improving drainage systems and implementing flood management plans.
Humanitarian Assistance
Local and international organizations are providing humanitarian assistance to flood victims in Nairobi, including:
- Food and shelter:Organizations are distributing food, water, and shelter to those displaced by the floods.
- Medical care:Organizations are providing medical care to flood victims, including treating waterborne diseases and injuries.
- Psychological support:Organizations are providing psychological support to flood victims, helping them cope with the trauma of the crisis.
Summary: Kenya Nairobi Flooding

Addressing the flooding crisis in Nairobi requires a comprehensive approach that tackles both the immediate challenges and the underlying causes. Long-term solutions, such as improving drainage systems, implementing sustainable urban planning, and investing in environmental conservation, are crucial to mitigate future flooding risks and ensure the safety and well-being of Nairobi’s residents.
FAQ Guide
What are the main causes of flooding in Nairobi?
Heavy rainfall, poor drainage systems, and inadequate urban planning contribute to the flooding in Nairobi.
How is the government responding to the flooding crisis?
The government is providing relief, evacuating residents, and addressing the underlying causes of flooding, including improving drainage systems and implementing sustainable urban planning.
What are the long-term solutions to address flooding in Nairobi?
Long-term solutions include infrastructure improvements, urban planning initiatives, and environmental conservation measures, such as improving drainage systems, implementing sustainable urban planning, and investing in environmental conservation.